Treatment of Newly Diagnosed Myeloma (excluding t-cell redirection therapy)
Category: Treatment of Newly Diagnosed Myeloma (excluding t-cell redirection therapy)
Daratumumab(Dara) Lenalidomide(R) maintenance following Dara-Carfilzomib(K)R Dexamethasone with tandem transplant in high-risk newly diagnosed myeloma patients: update of the phase 2 study IFM 2018-04
(PA-424) Daratumumab(Dara) Lenalidomide(R) Maintenance Following Dara-Carfilzomib(K)R Dexamethasone with Tandem Transplant in High-Risk Newly Diagnosed Myeloma Patients: Update of the Phase 2 Study IFM 2018-04

Bénédicte Piron, MD (she/her/hers)
Resident
Department of Hematology, University Hospital of Nantes, France
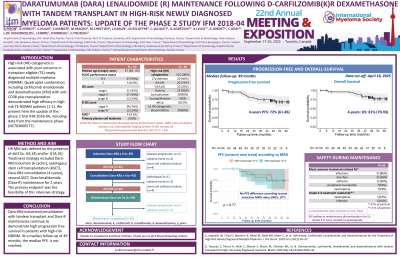
Methods: HR MM was defined by the presence of del17p, t(4;14) and/or t(14;16). Treatment strategy included Dara-KRd induction (6 cycles), autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT), Dara-KRd consolidation (4 cycles), second ASCT, Dara-lenalidomide (Dara-R) maintenance for 2 years. The primary endpoint was the feasibility of this intensive strategy.
Results:
Fifty patients with previously untreated NDMM were included from july 2019 to march 2021 in 11 IFM centers. Median age was 57 (range 38-65). Based on inclusion criteria, all patients had HR cytogenetic, including 17p deletion (n=20, 40%), t(4;14) (n=26, 52%) or t(14;16) (n=10, 20%). Four (8%) patients had extramedullary disease. Efficacy and safety profile of induction, transplant and consolidation were previously reported (Touzeau et al. Blood 2024). With a median follow-up of 49 months, twenty patients (40%) discontinued treatment, due to stem-cell collection failure (n=8), disease progression (n=7), adverse event (n=4), consent withdrawal (n=1). Among the 36 patients who entered the maintenance phase, 6 patients discontinued treatment (disease progression, n=5 ; grade 5 adverse event, n=1). Most common treatment related adverse events ( >15% of patients) during Dara-R maintenance were infections (86%), diarrhea (58%), asthenia (30%), peripheral neuropathy (19%) and neutropenia (19%). Grade 3-4 Dara-R maintenance related adverse events ( >5% of patients) were neutropenia (14%) and infections (16%). One patient discontinued maintenance due to severe adverse event (grade 5 JC virus related encephalopathy). At data cut-off, the 4-year progression free survival was 72% (61-86) and the 4-year overall survival was 81% (70-93). Among the 5 patients with disease progression during maintenance, 4 had negative pre-maintenance Minimal Residual Disease (MRD) (NGS, 10-6), suggesting that MRD negativity might not prevent early relapse at the individual level for patients with HR disease.
Conclusions:
Dara-KRd induction/consolidation with tandem transplant and Dara-R maintenance continue to demonstrate high progression free survival in patients with high-risk NDMM.
