Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory Myeloma (excluding T-cell redirection therapy)
Category: Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory Myeloma (excluding T-cell redirection therapy)
DARMMA – REAL LIFE EXPERIENCE OF THE USE OF DARATUMUMAB IN MULTIPLE MYELOMA IN PORTUGAL
(PA-498) DARMMA – Real Life Experience of the Use of Daratumumab in Multiple Myeloma in Portugal

Manuel Neves (he/him/his)
Hematologist
Serviço de Hemato-Oncologia, Fundação Champalimaud
Introduction:
Daratumumab (Dara) is an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody that demonstrated efficacy in the treatment of multiple myeloma (MM) in numerous clinical trials (CT). Real-world data provides an opportunity to study its use in clinical practice and to compare outcomes with those from CT.
Methods:
DarMMa is a national, multicentric, retrospective study to evaluate MM patients (pts) treated with Dara, in monotherapy or combinations, between November 2017 and December 2023. Response was evaluated by the IMWG criteria, high-risk cytogenetics (HRC) defined by the presence of del17p, t(4;14) or t(14;16). Progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method and multivariate analysis were performed using Cox regression.
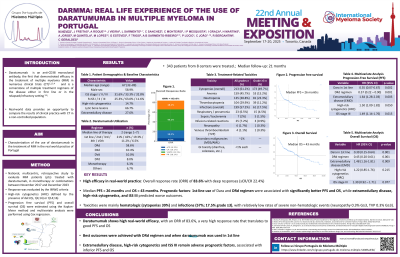
Results: A total of 343 pts were treated, 58.9% male, with a median age of 67yo (32-89); International Staging System (ISS) was I in 31.6%, II in 33.3% and III in 32.8%, unknown 2.3%. R-ISS available in 292 pts: I in 25.3%, II in 63.0%; III in 11.6% pts. Cytogenetic data were available for 55.5% of pts, 14.7% with HRC. Lytic bone lesions were observed in 66.7% and extramedullary disease (EMD) in 27.6% of pts. Treatment regimens included DRd 58.6%, DKd 10.4%; DVd 10%; DPd 8%; Dara monotherapy 6.3%. The median line of therapy in which daratumumab was administered was 2 (1-7) - 21% of pts had Dara in 1st line, 42% in 2nd line, 19.3% in 3rd line, 11.2% in 4th line, 6.5 in 5th or posterior. With a median follow up of 21 months, the overall response rate (ORR) was 83.6%: sCR 6.3%; CR 16.1%; VGPR 43.1%; PR 18.1%; SD in 7.7%; PD in 8.6%. Autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation after Dara was performed in 9.8% pts and only 1.7% were re-treated with Dara. Treatment discontinuation due to toxicity occurred in 9.2% of cases. Cytopenias occurred in 50.4% (33.3% grade ³ 3, with neutropenia grade ³3 23.3%) and infections in 50.5% pts (17,5% grade ³ 3). Median PFS was 26 months and median OS was 43 months. Dara in 1st line had superior PFS versus 2nd-3rd line (NR versus 27 months, p=0.001) and superior OS (median OS 44 vs 33 months, p=0.001). In multivariate analysis for PFS, treatment with Dara in 1st line (p = 0.002; HR 0.35) and use of DRd (p=0.001; HR 0.57) were associated with superior PFS, while EMD (p=0.003; HR 1.64), HRC (p=0.050; HR 1.48) and ISS 3 (p=0.015; HR = 1.49) were associated with worse PFS. In multivariate analysis for OS, treatment with Dara in 1st line (p = 0.001; HR 0.39) and use of DRd (p=0.001; HR 0.45) were associated with superior OS and EMD (p=0.009; HR 1.48) and ISS 3 (p=0.077; HR = 1,30) were associated with worse OS.
Conclusions:
The DarMMa study characterizes Dara use in Portugal, showing good ORR, PFS, OS, and tolerability in real-world practice. DRd was the most effective regimen, and 1st line treatment with Dara was associated with better outcomes.
