Imaging, QoL and Patient-Reported Outcome and Supportive Care
Category: Imaging, QoL and Patient-Reported Outcome and Supportive Care
Evaluating the Most Influential Factors in Decision-Making in Women and Men with Relapsed Multiple Myeloma
(PA-124) Evaluating the Most Influential Factors in Decision-Making in Women and Men with Relapsed Multiple Myeloma

Martha P. Anchondo Commesse, MD (she/her/hers)
Clinical Data Lead
HealthTree Foundation
Gender's influence on treatment decision-making in Refractory/Relapsed Multiple Myeloma (RRMM) presents complex healthcare challenges. This study analyzes gender-based factors affecting RRMM treatment choices.
Methods:
A survey was administered via HealthTree Cure Hub (PMID: 35271305) from February 14 to November 8, 2023. The 30-question survey assessed 11 decision-making domains at treatment changes, categorizing influential factors as treatment-related, patient-related, or myeloma-related. Participants rated influence using a 5-point scale (1 = not influential, to 5 = extremely influential). Patients with ≥1 relapse (RRMM) were stratified by gender (women [F], men [M]).
Results:
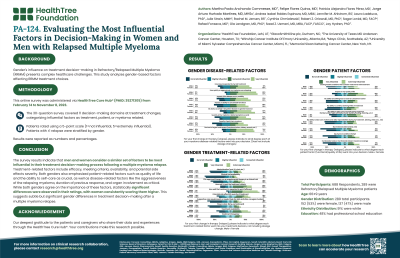
Of 688 survey respondents, 289 were RRMM patients (mean age: 66±9 years); 55% were female, 91% identified as White, 5% as Black, 6% as Hispanic or Latino/a, and 48% had a professional school education. Across all surveyed factors, women rated them as equally or more influential than men, with similar top-rated factors within each domain.
Among treatment-related factors, both men and women ranked the top four most influential as treatment efficacy (F: 4.3±1.0, M: 4.1±1.1, p< 0.05), meeting treatment criteria (F: 3.5±1.4, M: 3.3±1.3, p< 0.05), treatment availability (F: 3.4±1.5, M: 3.1±1.5, p< 0.05), and potential severity of side effects (F: 3.4±1.3, M: 3.2±1.1, p< 0.05).
Regarding patient-related factors, both groups ranked the top most influential as the impact on quality of life (F: 3.6±1.3, M: 3.2±1.3, p< 0.05) and the ability to care for themselves (F: 3.2±1.4, M: 2.9±1.4, p< 0.05).
In terms of myeloma-related factors, they ranked the top most influential as relapse aggressiveness (F: 3.3±1.8, M: 2.8±1.8, p< 0.05), duration of previous treatment response (F: 2.7±1.7, M: 2.5±1.6, p< 0.05), and level of organ involvement (F: 2.6±2.0, M: 2.3±1.9, p< 0.05).
Conclusions:
The survey results indicate that both men and women consider similar factors as the most influential in their treatment decision-making process following a multiple myeloma relapse. The treatment-related factors include treatment efficacy, meeting treatment criteria, treatment availability, and the potential severity of side effects. For patient-related factors, both genders emphasized the impact on quality of life and the ability to care for themselves as crucial. In the myeloma disease-related factors, they highlighted the aggressiveness of the relapsing myeloma, the duration of previous treatment response, and the level of organ involvement as critical. Statistically significant differences were observed between men and women in their ratings of all these factors, with women consistently rating them slightly higher.
