Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory Myeloma (excluding T-cell redirection therapy)
Category: Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory Myeloma (excluding T-cell redirection therapy)
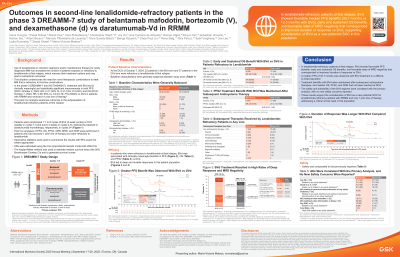
Outcomes in Second-Line Lenalidomide-Refractory Patients in the Phase 3 DREAMM-7 Study of Belantamab Mafodotin, Bortezomib (V), and Dexamethasone (d) vs Daratumumab-Vd in RRMM
(PA-494) Outcomes in Second-Line Lenalidomide-Refractory Patients in the Phase 3 DREAMM-7 Study of Belantamab Mafodotin, Bortezomib (V), and Dexamethasone (d) vs Daratumumab-Vd in RRMM

María-Victoria Mateos, MD, PhD
Consultant Physician, Associate Professor of Medicine
Hematology Department, University Hospital of Salamanca/IBSAL/Cancer Research Center-IBMCC (USAL-CSIC), Salamanca, Spain
Use of lenalidomide (len) in induction regimens and/or maintenance therapy for newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (MM) has increased the number of patients (pts) exposed to or refractory to len at their first relapse, which narrows their treatment options and may lead to suboptimal outcomes. This underscores the need for novel therapeutic combinations to treat MM that is refractory to first-line combinations. The phase 3 DREAMM-7 trial (NCT04246047) compares belantamab mafodotin (belamaf), bortezomib, and dexamethasone (BVd) vs daratumumab, bortezomib, and dexamethasone (DVd) in pts with relapsed or refractory MM (RRMM) who have received ≥1 prior line of therapy (LOT). DREAMM-7 has previously demonstrated significant and clinically meaningful progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) benefits with BVd in comparison to DVd. This post hoc analysis examines outcomes in the subpopulation of len-refractory pts at first relapse.
Methods:
Pts were randomized 1:1 to 8 cycles of BVd (3-week cycles) or DVd (weekly in cycles 1-3 and every 3 weeks in cycles 4-8), followed by belamaf or daratumumab monotherapy, respectively, in cycles 9+. Post hoc analyses of PFS, OS, and duration of response (DOR) were performed in pts who had received 1 prior LOT and were refractory to len. Hazard ratios (HRs) were estimated using the Cox model with Wald CIs. The Kaplan-Meier method was used to compute medians with 95% Brookmeyer-Crowley CIs.
Results: Approximately half of pts in the intention-to-treat (ITT) population (BVd, 124/243; DVd, 125/251) had only 1 prior LOT, 52% (257/494) had prior len, and 33.6% (166/494) were refractory to len; 21 BVd pts and 27 DVd pts were refractory to len at first relapse. In second-line len-refractory BVd pts, a median PFS of 35.7 mo (95% CI, 17.5 mo-not estimable [NE]) was observed vs 13.5 mo (95% CI, 6.6-26.3 mo) in DVd pts (HR, 0.39; 95% CI, 0.17-0.88). The estimated 24-month PFS was 67% (95% CI, 41%-84%) vs 35% (95% CI, 17%-53%) in the BVd and DVd groups, respectively. At data cutoff (October 7, 2024), 8 (38%) and 12 (44%) pts had died in the BVd and DVd arms, respectively. The median OS was not reached (NR; 95% CI, 35.7 mo-NE) with BVd vs 35.4 mo (95% CI, 24.4 mo-NE) with DVd (HR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.26-1.59). The 36-month OS rate was 74% with BVd and 50% with DVd. Median DOR was NR (95% CI, 16.2 mo-NE) with BVd vs 13.1 mo (95% CI, 7.0 mo-NE) with DVd. Additional findings will be presented at the meeting.
Conclusions:
In len-refractory pts at first relapse, BVd showed favorable PFS benefits, early and sustained OS benefits, and durable responses vs DVd. These results support the consideration of BVd as a new potential standard of care for len-refractory pts with RRMM and only 1 prior LOT, addressing a critical unmet need in this population.
Funding: GSK (207503). Drug-linker technology licensed from Seagen Inc; monoclonal antibody produced using POTELLIGENT Technology licensed from BioWa.
