Cellular and T cell engager Immunotherapy
Category: Cellular and T cell engager Immunotherapy
Economic Value of Tocilizumab Prophylaxis to Prevent Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS) during Outpatient Teclistamab (Tec) or Talquetamab (Tal) Initiation for Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma (RRMM)
(PA-008) Economic Value of Tocilizumab Prophylaxis to Prevent Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS) During Outpatient Teclistamab (Tec) or Talquetamab (Tal) Initiation for Relapsed/refractory Multiple Myeloma (RRMM)
- NG
Introduction:
Tec and Tal are bispecific antibodies approved for triple class-exposed RRMM, based on high overall response rates in the MajesTEC-1 (TEC-1) and MonumenTAL-1 (TAL-1) trials, respectively. Due to risk of CRS at initiation, step-up doses (SUDs) should be administered in the inpatient setting per label. However, several studies have shown outpatient administration of SUDs that can reduce healthcare resource utilization to be feasible, and prophylactic use of tocilizumab can be used to facilitate outpatient SUDs by reducing CRS incidence and severity. Early data from the Phase 2 OPTec study showed that only 6.25% (1/16) experienced grade [Gr] 1 CRS and none experienced Gr 2+ CRS when tocilizumab was administered before the first outpatient Tec SUD. The present study assessed the economic impact of adopting prophylactic tocilizumab to support outpatient administration of Tec or Tal, from a United States healthcare institution perspective.
Methods:
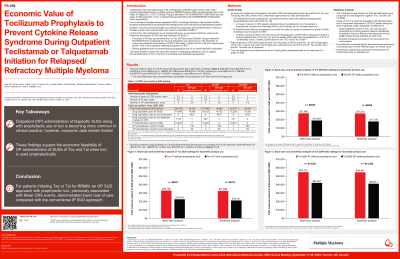
An economic model was developed to calculate costs for Tec and Tal during the SUD period under two alternative approaches for SUD administration: (1) outpatient administration with prophylactic tocilizumab (ACTEMRA®) before the first SUD (additionally, for Tal, prophylactic dexamethasone after each SUD); or (2) inpatient administration (with tocilizumab only as reactive treatment of Gr 2+ CRS, including recurrent Gr 2+ CRS). The two approaches were compared for each bispecific regimen: Tec, Tal weekly (QW), and Tal biweekly (Q2W). Patients with Gr 2+ CRS despite prophylactic tocilizumab were assumed to receive all remaining SUDs inpatient and retreated with tocilizumab. Risks of Gr 2+ CRS were based on OPTec (Tec) or a sub-analysis of TAL-1 (Tal) under the outpatient approach, and TEC-1 (Tec) or TAL-1 (Tal) under the inpatient approach. Costs of Tec, Tal and tocilizumab acquisition, outpatient administration, and inpatient stays were estimated in 2025$ based on trial data, drug labels, public databases, and literature. Pre-medication and prophylactic dexamethasone costs were not included due to minimal impact. A sensitivity analysis was conducted using the price of tocilizumab-aazg (TYENNE®), a biosimilar tocilizumab.
Results:
Total per-patient costs under the outpatient versus inpatient approaches were estimated to be, respectively, $18,797 vs. $27,639 (difference: -$8,841) for Tec, $18,419 vs, $26,964 (difference: -$8,545) for Tal QW, and $40,767 vs, $53,388 (difference: -$12,621) for Tal Q2W. Cost differences were largely attributable to fewer inpatient days under the outpatient approach. The cost savings with outpatient (vs. inpatient) SUDs were even greater in sensitivity analyses that used biosimilar tocilizumab pricing (Tec: -$9,725; Tal QW/Q2W: -$9,506/-$13,586).
Conclusions:
For patients initiating Tec or Tal for RRMM, an outpatient SUD approach with prophylactic tocilizumab was associated with lower costs of care than the conventional inpatient SUD approach.
