MRD and Biomarkers
Category: MRD and Biomarkers
Testing and validating a mass spectrometry based algorithm for response assessment in myeloma
(PA-165) Testing and Validating a Mass Spectrometry Based Algorithm for Response Assessment in Myeloma

Lauren Campbell, PhD (she/her/hers)
Clinical Scientist
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust
Introduction:
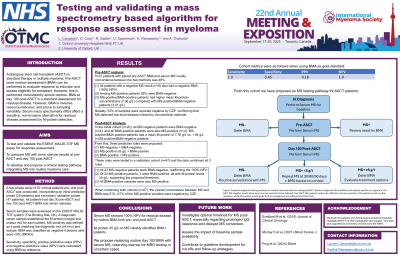
Bone marrow aspirate (BMA) at day 100 post-autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) is a standard assessment for residual disease in multiple myeloma, but is invasive, resource-intensive, and prone to sampling variability. As deeper responses are increasingly seen a less invasive but sensitive test is needed. Serum mass spectrometry (MS) offers a highly sensitive, non-invasive alternative. We evaluated the EXENT MALDI-TOF MS assay as a potential replacement for BMA at day 100 post-ASCT.
Methods:
A two-phase study of 67 clinical patients post-ASCT was conducted, incorporating an initial prediction phase and secondary validation phase. All had day 100 BMA and serum samples. A diagnostic serum sample established the M-protein isotype and unique m/z for each patient. MS positivity was defined as a peak matching the diagnostic m/z (±4 m/z) and isotype. BMA was classified as negative if plasma cells were < 5% (IMWG). Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) were calculated using BMA as reference.
Results:
In the initial cohort (n=20), all MS-negative patients were BMA-negative (n=4), and all BMA-positive patients were also MS-positive (n=4). MS-positive/BMA-positive patients had a mean M-protein of 7.76 g/L vs. 1.94 g/L in MS-positive/BMA-negative patients. From this, three predictive rules were proposed: (1) MS-negative = BMA-negative, (2) MS-positive ≥5 g/L = BMA-positive, (3) BMA-positive = MS-positive.
These rules were tested in a validation cohort (n=47). All 23 MS-negative patients were BMA-negative, reaffirming the 100% NPV. Of 24 MS-positive patients, 3 were BMA-positive, all with M-protein levels ≥5 g/L, supporting the proposed threshold. All BMA-positive samples were also MS-positive (n=7), validating rule (3).
When combining both cohorts (n=67), the overall concordance between MS and BMA was 51%. 67% of the MS-positive samples were negative by CZE. Cohort metrics were as follows when using BMA as gold standard: sensitivity 100%, specificity 45%, PPV 18%, NPV 100%. From this cohort we have proposed an MS testing pathway for ASCT patients:
- Perform baseline serum MS at diagnosis to identify M-protein m/z.
- Perform serum MS at day 100 post-ASCT for all patients as first-line test.
- If MS-negative: omit BMA and continue routine surveillance.
- If MS-positive ≥5 g/L: interpret as highly likely BMA-positive and consider treatment options.
- If MS-positive < 5 g/L: review in clinical context and perform serial MS monitoring to closely track M-protein changes.
Conclusions:
The EXENT MS assay shows 100% NPV for BMA-defined residual disease at day 100 post-ASCT, identifying all patients with negative BMA while avoiding invasive procedures. We propose replacing routine BMA with serum MS for CR assessment, reserving BMA only for MRD assessment by more sensitive methods.
